Ebury Botnet Malware Infects 400,000 Systems Worldwide
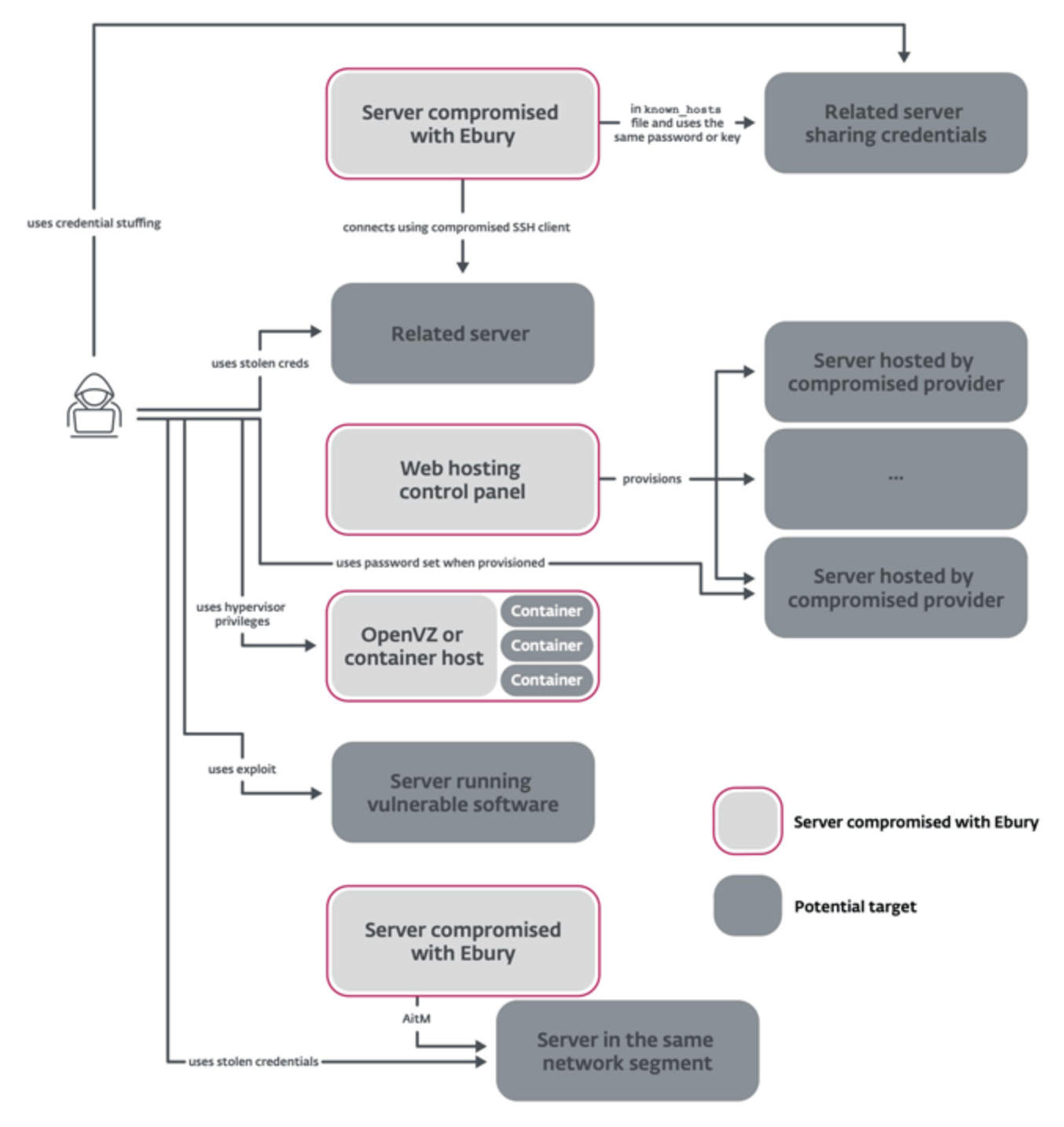
The Ebury botnet malware has already infected over 400,000 systems globally, now becoming a major threat to the cybersecurity of companies throughout the world. Although a botnet focused on infecting primarily Linux servers, Ebury has caused a major-scale infection over the course of quite a sophisticated campaign that has lasted considerably long until the darkness of the detection. Still, by its ability to do everything sneaky and in a sophisticated swell-busting manner, Ebury malware has risen to be a high-strung threat to cybersecurity professionals. However, the most alarming aspect of the Ebury botnet is its stealing SSH credentials, allowing unauthorized entry to the systems; as soon as it bores into the server, it installs a rootkit to remain inconspicuous. Moreover, the malware creates a backdoor in the system, allowing the controllers a free hand to the systems of their victims. They, thus, have the ability to utilize the infected servers for any sort of nefarious activity on the internet, including sending spam, doing DDoS attacks, and even for executing the click fraud.
The Ebury botnet operators are technically sound and demonstrate considerable coordination. They have used many techniques of spreading the malware, including the exploitation of vulnerabilities in some older versions of the software and gaining access to the systems by brute force attacks. Additionally, the Ebury botnet operators were found to be switching command and control servers quite frequently to make the operations hard to shut down. Still, work is in progress on the crackdown on the Ebury botnet, with coordination between companies specializing in cybersecurity and enforcement agencies on one end and those responsible for the research to bring forward the tools to trace and clean this malware on the other end. Researchers have used this to analyze the code of the malware and its behavior to develop effective detections and removal tools. All these efforts, yet the botnet still remains very persistent. This means that organizations have to maintain a strong security posture in terms of updates and good password policies.
The effects of Ebury do not stop at its victims only; definitely, attackers can use the compromised servers to attack other targets. It just reinstates the fact that it has to be a combined effort to elevate the cybersecurity measures and keep all these threats out from critical infrastructures. Just as the Ebury botnet illustrated, criminals adjust their tactics to keep victimizing users, and this means the cybersecurity community needs to be proactive in ensuring that users are protected from all these next-generation threats.